Table of Contents
ToggleIntro
Importance of lithium batteries
In today’s world, lithium-ion batteries have become an integral part of our lives, powering everything from smartphones and laptops to electric vehicles and energy storage systems. As the demand for these batteries continues to soar, ensuring their quality and safety has become a top priority for manufacturers.
Quality control challenges
However, the production of lithium-ion batteries is a complex process, and even the slightest defect can compromise the battery’s performance or, worse, pose a safety risk. This is where X-ray testing comes into play, offering a non-destructive and highly effective method for quality control.
X-Ray Testing for Lithium Batteries
What is X-ray testing?
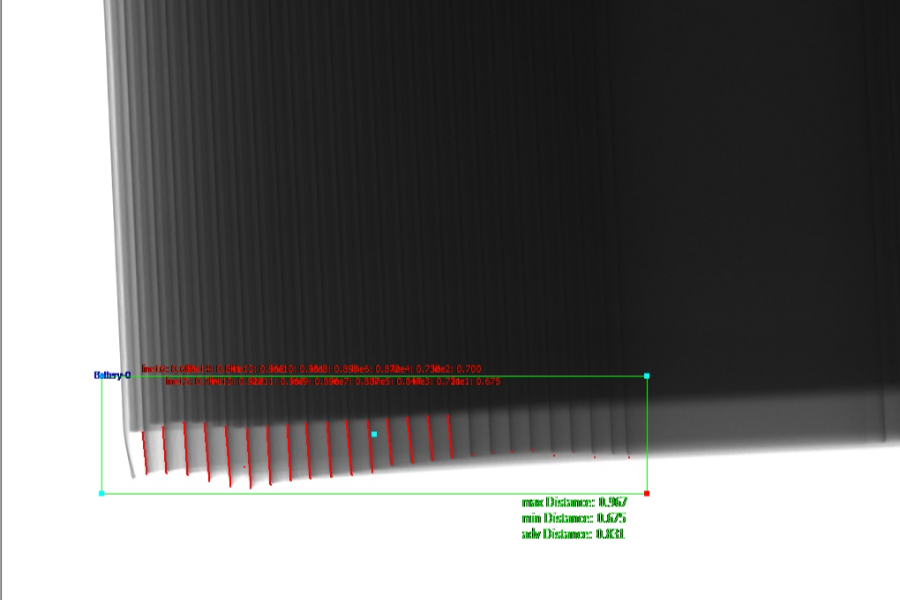
X-ray testing, also known as radiographic inspection, is a non-destructive testing technique that uses high-energy electromagnetic radiation to penetrate and inspect materials. In the context of lithium battery production, X-ray testing can reveal defects such as delamination, foreign objects, and component misalignments within the battery cells.
Benefits of X-ray testing
One of the primary advantages of X-ray testing is its ability to detect internal defects without damaging the battery cells. This non-destructive nature makes it an ideal solution for quality control, as it allows manufacturers to inspect every single battery without compromising its integrity. Additionally, X-ray testing is a highly accurate and reliable method, capable of detecting even the smallest defects that might be missed by other inspection techniques.
Applications in Lithium Battery Production
Incoming material inspection
X-ray testing plays a crucial role in the incoming material inspection process. Before raw materials are used in battery production, they are subjected to X-ray inspection to ensure they meet the required quality standards. This step helps identify any defects or contaminants that could potentially compromise the performance or safety of the final product.
In-process inspection
During the manufacturing process, X-ray testing is used to monitor the quality of the battery cells at various stages. This includes inspecting the electrode assembly, electrolyte filling, and sealing processes. By detecting defects early on, manufacturers can take corrective actions and prevent further waste of resources.
Final product inspection
Before lithium-ion batteries are shipped to customers, they undergo a final X-ray inspection. This step ensures that the finished product meets all quality and safety standards, reducing the risk of recalls and potential legal liabilities.
Key Challenges
While X-ray testing offers numerous benefits for lithium battery production, it also comes with its own set of challenges.
Safety concerns
X-ray radiation, if not properly controlled, can be harmful to human health. As such, strict safety protocols and shielding measures must be in place to protect workers from excessive exposure. This adds to the overall cost and complexity of implementing X-ray testing systems.
Equipment cost
X-ray testing equipment can be expensive, especially for large-scale battery production facilities. The initial investment, as well as ongoing maintenance and repair costs, can be substantial.
Skilled labor requirements
Operating and interpreting X-ray testing equipment requires specialized training and expertise. Manufacturers must invest in skilled technicians and establish robust training programs to ensure accurate and consistent results.
Conclusion
As the lithium battery industry continues to grow, the need for effective quality control measures becomes increasingly important. X-ray testing offers a powerful solution for detecting defects and ensuring the safety and reliability of these batteries. While challenges such as safety concerns, equipment costs, and skilled labor requirements exist, the benefits of X-ray testing outweigh the drawbacks, making it an essential tool for manufacturers committed to delivering high-quality products.
FAQs
1. Can X-ray testing detect all types of defects in lithium batteries?
X-ray testing is highly effective in detecting a wide range of defects, including delamination, foreign objects, and component misalignments. However, it may not be suitable for detecting certain types of defects, such as chemical or electrical issues. Other testing methods may be required to complement X-ray testing for a comprehensive quality control program.
2. Is X-ray testing suitable for all types of lithium batteries?
X-ray testing can be used for various types of lithium-ion batteries, including cylindrical, prismatic, and pouch cells. However, the specific testing parameters and equipment configurations may need to be adjusted based on the battery’s size, shape, and construction.
3. How long does X-ray testing take?
The time required for X-ray testing can vary depending on the size of the battery, the complexity of the inspection, and the throughput requirements of the production line. In general, modern X-ray testing systems can inspect batteries at high speeds, minimizing the impact on production rates.
4. Are there any alternatives to X-ray testing for lithium battery inspection?
While X-ray testing is widely used, other non-destructive testing methods, such as ultrasonic testing and computed tomography (CT) scanning, can also be employed for lithium battery inspection. The choice of method depends on factors such as the type of defects being targeted, cost considerations, and production requirements.
5. How often should X-ray testing equipment be calibrated or maintained?
Regular calibration and maintenance of X-ray testing equipment are essential to ensure accurate and reliable results. The frequency of calibration and maintenance depends on factors such as the equipment manufacturer’s recommendations, usage patterns, and regulatory requirements. Typically, calibration is performed periodically, while maintenance tasks like detector cleaning and source replacement may be required more frequently.